Page 191 - CW E-Magazine (3-12-2024)
P. 191
Special Report
solutions. These results generally show
the corrosion rates to decrease with
increasing nickel content in the alloy.
It should be mentioned that the weight
loss data obtained with 310 SS, Ni, and
high Ni alloys are not reliable, as they
passivate in hot 50% NaOH solutions.
The reason for the high corrosion rates
of Fe-Cr-Ni alloys was found to be
the preferential dissolution of Fe and
Cr. Cu dissolves from Monel 400 and
Mo from Mo-containing alloys such
as Type 316 SS and alloy 825 in hot
concentrated NaOH.
The corrosion behaviour of nickel-
based alloys was significantly influen-
ced by thepresence of oxygen or
hydrogen in the solution. These mate-
rials exhibited reversible hydrogen elec-
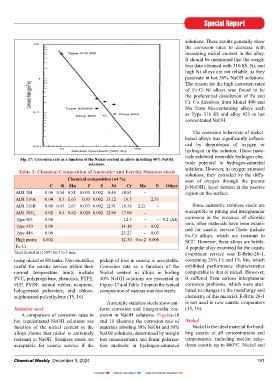
Fig. 17: Corrosion rate as a function of the Nickel content in alloys in boiling 40% NaOH
solutions. trode potential in hydrogen-saturated
Table 3: Chemical Composition of Austentic and Ferritic Stainless steels solutions. However, in oxygen saturated
a
solutions, they corroded by the diffu-
Chemical composition (wt %) sion of oxygen through the porous
C Si Mn P S Ni Cr Mo N Other β-Ni(OH) layer formed in the passive
2
AISI 304 0.06 0.54 0.81 0.031 0.002 8.48 18.91 – region on the surface.
AISI 316A 0.04 0.5 1.63 0.03 0.002 13.12 16.5 2.35
AISI 316B 0.06 0.45 1.67 0.033 0.002 12.91 16.58 2.21 – Since austenitic stainless steels are
AISI 305J 0.02 0.4 0.82 0.029 0.002 12.96 17.08 – susceptible to pitting and intergranular
1
Type 405 0.08 12.5 – – 0.2 (AI) corrosion in the presence of chloride
Type 430 0.08 14-18 – 0.02 ions, other materials have been exami-
Type 446 0.08 23-27 – 0.03 ned for caustic service.These include
Fe-Cr alloys, which are resistant to
High purity 0.002 12-30 0 to 2 0.008 SCC. However, these alloys are brittle.
Fe-Cr A popular alloy examined for the caustic
a Heat treated at 1150 C for 3 to 5 min. evaporator service was E-Brite-26-1,
o
using nickel or SS tanks. Non-metallics pickup of iron in caustic is acceptable. containing 26% Fe and 1% Mo, which
useful for caustic service within their Corrosion rate as a function of the exhibited performance characteristics
normal temperature limits include Nickel content in alloys in boiling comparable to that of nickel. However,
PVC, polypropylene, phenolics, PTFE, 40% NaOH solutions are presented in it suffered from serious intergranular
FEP, PVDF, natural rubber, neoprene, Figure-17 and Table-3 depicts the typical corrosion problems, which were attri-
halogenated polyesters, and chloro- composition of various stainless steels. buted to changes in the metallurgy and
sulphonated polyethylene (15, 16). chemistry of this material. E-Brite 26-1
Austenitic stainless steels show uni- is not used in new caustic evaporators
Stainless steel form corrosion and intergranular cor- (15, 16).
A comparison of corrosion rates in rosion in NaOH solutions. Figures-18
hot concentrated NaOH solutions asa and 19 illustrate the corrosion rate of Nickel
function of the nickel content in the materials inboiling 30% NaOH and 50% Nickel is the ideal material for hand-
alloys shows that nickel is extremely NaOH solutions, determined by weight ling caustic at all concentrations and
resistant to NaOH. Stainless steels are loss measurements and linear polariza- temperatures, including molten anhy-
acceptable for caustic service if the tion methods in hydrogen-saturated drous caustic up to 480°C. Nickel and
Chemical Weekly December 3, 2024 191
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised