Page 185 - CW E-Magazine (10-9-2024)
P. 185
Special Report Special Report
resist the effects of water transmission pipe wall. The soil that surrounds the in the soil. It has been found that low all SCC features within the pipe seg-
and cathodic disbondment. pipe can move and is another source of pH SCC occurs in environments with Failure ment is more signifi cant than the maxi-
stress. Pipe manufacturing processes, a low concentration of carbonic acid mum pressure obtained during the test.
There are several factors relating to such as welding, can also create stresses. and bicarbonate ions with the presence Single SCC features that fail the pres-
soils that infl uence the formation of an These are called residual stresses. of other species, including chloride, sure test can be characterized entirely
environment that’s conducive to SCC. sulphate and nitrate ions. Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 concerning the failure pressure, pipe
These are soil type, drainage, carbon Types of SCC material properties, physical SCC
dioxide (CO ), temperature and electri- SCC in pipelines is characterized Typically, the SCC colonies initi- dimensions, in-depth SCC interaction,
2
cal conductivity. The amount of mois- as “high pH SCC” or “near-neutral pH ate at locations on the outside surface, Crack growth rate and length directions. SCC most likely
ture in the soil also affects the forma- SCC.” Note that the “pH” here refers where there is already pitting or general to fail is typically composed of several
tion of SCC. to the environment on the pipe surface corrosion. This damage is sometimes fused features with little likelihood
at the crack location, not the pH of the obvious to the unaided eye, while at Initiation of further coalescence. The quantity,
The presence of Cathodic Protec- soil itself. other times it is very diffi cult to conditions Cracks Growth by continuous initiation, Large cracks density and location of SCC features
coalescence
extension, and coalescence
initiate
tion (CP) current is a key factor in the observe. develop that do not fail within a pipe segment
formation of a carbonate/bicarbonate High pH SCC (classic type) Time remain unknown. If no SCC failure
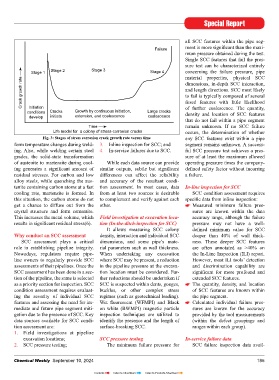
environment at the pipeline surface, High pH SCC occurs on the exter- The near-neutral-pH form of SCC Life model for a colony of stress-corrosion cracks occurs, the determination of whether
where high pH SCC occurs. For near- nal surface of pipelines where the elec- is trans-granular; the cracks propagate Fig. 3: Stages of stress corrosion crack growth rate versus time any SCC features exist within a pipe
neutral pH, SCC CP is absent. Tempe- trolyte in contact with the pipe surface through the grains in the metal and are form temperature changes during weld- 3. Inline inspection for SCC; and segment remains unknown. A success-
rature has a signifi cant effect on the has a pH of 8-11 and the concentration wider (more open) than in the high-pH ing. Also, while welding certain steel 4. In-service failures due to SCC. ful SCC pressure test achieves a pres-
occurrence of high pH SCC, while it of carbonate/bicarbonate is very high. form of SCC. In other words, the crack grades, the solid-state transformation sure of at least the maximum allowed
has no effect on near-neutral pH SCC. This electrolyte is found at disbonded sides have experienced metal loss from of austenite to martensite during cool- While each data source can provide operating pressure times the company-
areas of coatings where the CP current corrosion. Near-neutral-pH SCC is less ing generates a signifi cant amount of similar outputs, subtle but signifi cant defi ned safety factor without incurring
A material susceptible to SCC is insuffi cient to protect the pipeline. temperature-dependent than high-pH residual stresses. For carbon and low differences can affect the reliability a failure.
In addition to a potent environ- This type of SCC may develop as a SCC. alloy steels, while quenching the aus- and accuracy of the resultant condi-
ment, a susceptible pipe material is result of the interaction between tenite containing carbon atoms at a fast tion assessment. In most cases, data In-line inspection for SCC
another necessary condition in the hydroxyl ions produced by the cathode How crack growth occurs cooling rate, martensite is formed. In from at least two sources is desirable SCC condition assessment requires
development of SCC. A number of pipe reaction and CO in the soil generated The SCC phenomenon has four key this situation, the carbon atoms do not to complement and verify against each specifi c data from inline inspection:
2
characteristics and qualities are consi- by the decay of organic matter. stages: get a chance to diffuse out from the other. Measured minimum failure pres-
dered to determine if they are possibly 1. Initiation of cracks; crystal structure and form cementite. sures are known within the data
related to the susceptibility of a pipe This form of SCC is temperature- 2. Slow growth of cracks; This increases the metal volume, which Field investigation at excavation loca- accuracy range, although the failure
to SCC. These factors include the pipe sensitive and occurs more frequently 3. Coalescence of cracks; and results in signifi cant residual stress(6). tion (In-the-ditch-inspection for SCC) pressure may not have a well-
manufacturing process, type of steel, at higher temperature locations above 4. Crack propagation and structural It allows measuring SCC colony defi ned minimum value for SCC
grade of steel, cleanliness of the steel 38°C. This is why there is a greater failure. Why conduct an SCC assessment density, interaction and individual SCC deeper than 40% of wall thick-
(presence or absence of impurities or likelihood of SCC immediately down- SCC assessment plays a critical dimensions, and some pipe’s mate- ness. These deeper SCC features
inclusions), steel composition, plastic stream of the compressor stations This process can take many years role in establishing pipeline integrity. rial parameters such as wall thickness. are often annotated as >40% on
deformation characteristics of the steel where the operating temperature might depending on the conditions of the Nowadays, regulators require pipe- When undertaking any excavation the In-Line Inspection (ILI) report.
(cyclic-softening characteristics), steel reach 65°C. steel, the environment and the stresses line owners to regularly provide SCC where SCC may be present, a reduction However, most ILI tools’ detection
temperature and pipe surface condition. to which a pipeline is subjected. Con- assessments of their pipelines. Once the in the pipeline pressure at the excava- and discrimination capability are
The high-pH form of SCC is sequently, failure as a result of SCC is SCC assessment has been done in a sec- tion location must be considered. Fur- signifi cant for more profound and
A tensile stress that’s higher than intergranular – the cracks propagate relatively rare, although failures can be tion of the pipeline, the same is selected ther reductions should be undertaken if extended SCC features.
threshold stress between the grains in the metal, and very costly and destructive when they as a priority section for inspection. SCC SCC is suspected within dents, gouges, The quantity, density, and location
When tensile stress is higher than there is usually little evidence of general do occur. Figure-3 illustrates the life condition assessment requires evaluat- buckles, or other complex stress of SCC features are known within
threshold stress, this can lead to SCC, corrosion associated with the cracking. model for a colony of SCC showing ing the severity of individual SCC regimes (such as geotechnical loading). the pipe segment.
especially when there is some dynamic These cracks are very tight and narrow. stages of crack growth rate versus time features and assessing the need for im- Wet fl uorescent (WFMPI) and Black Calculated individual failure pres-
or cyclic component to the stress. Stress (4, 5). mediate and future pipe segment miti- on white (BWMPI) magnetic particle sures are known for the accuracy
is the “load” per unit area within the Near-neutral pH SCC (non-classic type) gation due to the presence of SCC. Key inspection techniques are utilized to provided by the tool measurements
pipe wall. A buried pipeline is subject A near-neutral pH SCC environ- SCC in welding data sources available for SCC condi- identify the presence and the length of (within the defect groupings and
to different types of stress from dif- ment appears to be a dilute groundwater The major cause attributed to SCC tion assessment are: surface-breaking SCC. ranges within each group).
ferent sources. The pipeline’s contents containing dissolved CO . The source is the residual stress generated dur- 1. Field investigations at pipeline
2
are under pressure and that is normally of the CO is typically the decay of ing welding and fabrication processes. excavation locations; SCC pressure testing In-service failure data
2
the greatest source of stress on the organic matter and geochemical reactions SCC in welding is caused by non-uni- 2. SCC pressure testing; The minimum failure pressure for SCC failure inspection data avail-
184 Chemical Weekly September 10, 2024 Chemical Weekly September 10, 2024 185
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised