Page 190 - CW E-Magazine (10-9-2024)
P. 190
Special Report
The influence of alloy composition
160
on SCC
Resistance to chloride SCC depends
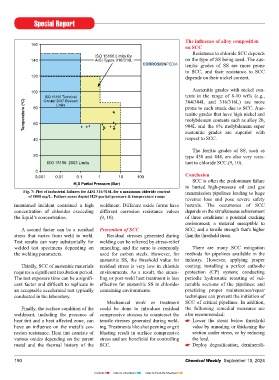
ISO 15156 Limits for
140 AISI Types 316/316L on the type of SS being used. The aus-
CORROSIONPEDIA tenitic grades of SS are more prone
to SCC, and their resistance to SCC
120 depends on their nickel content.
Austenitic grades with nickel con-
100
ISO 15156 Technical tents in the range of 8-10 wt% (e.g.,
Temperature ( o C) 80 prone to such attack due to SCC. Aus-
Circular 2007 Revised
304/304L and 316/316L) are more
Limits
tenitic grades that have high nickel and
molybdenum contents such as alloy 20,
60
904L and the 6% molybdenum super
austenitic grades are superior with
40 respect to SCC.
The ferritic grades of SS, such as
20 type 430 and 444, are also very resis-
ISO 15156: 2003 Limits tant to chloride SCC.(9, 10).
0
0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 Conclusion
SCC is often the predominant failure
H S Partial Pressure (Bar) in buried high-pressure oil and gas
2
Fig. 7: Plot of industrial failures for AISI 316/316L for a maximum chloride content transmission pipelines leading to huge
of 1000 mg/L. Failure zones depict H2S partial pressure & temperature range
revenue loss and pose severe safety
mentioned incident contained a high weldment. Different oxide forms have hazards. The occurrence of SCC
concentration of chlorides exceeding different corrosion resistance values depends on the simultaneous achievement
the liquid’s concentration. (9, 10). of three conditions: a potential cracking
environment; a material susceptible to
A second factor can be a residual Prevention of SCC SCC; and a tensile strength that’s higher
stress that varies from weld to weld. Residual stresses generated during than the threshold stress.
Test results can vary substantially for welding can be relieved by stress-relief
welded test specimens depending on annealing, and the same is commonly There are many SCC mitigation
the welding parameters. used for carbon steels. However, for methods for pipelines available in the
austenitic SS, the threshold value for industry. However, applying proper
Thirdly, SCC of austenitic materials residual stress is very low in chloride coating; installing a perfect cathodic
requires a significant incubation period. environments. As a result, the annea- protection (CP) system; conducting
The test exposure time can be a signifi- ling or post-weld heat treatment is less periodic hydrostatic retesting of vul-
cant factor and difficult to replicate in effective for austenitic SS in chloride- nerable sections of the pipelines; and
an acceptable accelerated test typically containing environments. practicing proper maintenance/repair
conducted in the laboratory. techniques can prevent the initiation of
Mechanical work or treatment SCC of critical pipelines. In addition,
Finally, the surface condition of the could be done to introduce residual the following remedial measures are
weldment, including the presence of compressive stresses to counteract the also recommended:
heat tint and a heat affected zone, can tensile stresses generated during weld- Lower the stress below threshold
have an influence on the metal’s cor- ing. Treatments like shot peening or grit value by annealing or thickening the
rosion resistance. Heat tint consists of blasting result in surface compressive section under stress, or by reducing
various oxides depending on the parent stress and are beneficial for controlling the load.
metal and the thermal history of the SCC. Deploy degasification, deminerali-
190 Chemical Weekly September 10, 2024
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised