Page 176 - CW E-Magazine (16-7-2024)
P. 176
Special Report Special Report
Algae biofuel integrated project can substitute petro- Table 2: Comparison of open pond and photo-bioreactors for algae cultivation of solar energy (in theory about
Parameter Open pond Photobioreactor 10% of the total solar energy can be
fi xed into biomass);
leum diesel and promote rural employment Contamination risk High Low Take sunlight and CO and make
2
Preamble to produce biofuel, which can substi- N.S. VENKATARAMAN Water & CO losses High Low long chains of oil that can be con-
2
lgae is a quick growing crop tute petroleum diesel. Director Process control Complicated Less complicated verted to biodiesel;
that contains around 20-25% Nandini Consultancy Centre Yield Low High Oil yield per area of microalgae
Aoil, depending upon the species. By digesting the algae biomass Chennai - 600 090 Construction costs Low High cultures greatly exceed the yield of
after extraction of oil, methane gas can Email: nsvenkatchennai@gmail.com Weather dependence High Low best oilseed crops;
Algae crop does not come in con- be produced and used for power (electri- By digesting algae biomass, bioetha- Can be cultivated in saline/brackish
fl ict with food crops, as it can be cul- city) generation. nol can also be produced, which can Overheating problems Low High water/coastal seawater on non-
tivated in saline water, brackish water, be blended with petrol. Dissolved oxygen concentration Low High arable land and do not compete for
coastal seawater, and on non-arable/ Table 1: Oil yield comparison of resources with conventional agri-
marshy land. oilseeds and algae Cultivation of algae closed ponds, in photo bioreactors, and Keeping out contaminants and culture;
[Litres per hectare] Algae species, rich in carbo- in hybrid systems, which combine open controlling the growth conditions are Utilise nitrogen and phosphorus
To cultivate and grow algae, tropi- Feedstock Oil yield hydrates, are grown in an aquaculture and closed systems. important factors for ensuring high yield. from a variety of wastewater sour-
cal conditions and good sunshine are Soybean 450 environment. The algae crop has no roots, ces (e.g., agricultural run-off, con-
required, which are available in most Rapeseed 1,190 leaves, or shoots. It is a quick-growing The inputs needed for the cultiva- Algae oil extraction centrated animal feed operations
parts of India. Algae cultivation also Mustard 575 crop (1-3 doublings per day), and the tion of algae are: About 70-75% of oil present in the and industrial and municipal waste-
requires carbon dioxide (CO ) and can Jatropha 1,600 to 1,800 average up to harvesting is only around Light – for photosynthesis; algae crop can be extracted in an oil waters), providing the additional
2
be seen as a form of carbon capture. four weeks. Different algae species, Medium/nutrients – composition of expeller/press. The remaining pulp can benefi t of wastewater bioremedia-
Palm oil 6,000 however, have different growth charac- water is an important consideration be mixed with cyclohexane to extract tion; and
From algae crop, oil can be extracted Algae 95,000 teristics, but are cultivated in open or (including salinity); the remaining oil content. Cold press Utilise CO from fl ue gases emitted
2
Aeration – Algae need to have con- and solvent extraction (using hexane as from fossil fuel fi red power plants
tact with air; solvent) together will extract more than and other sources, thereby reducing
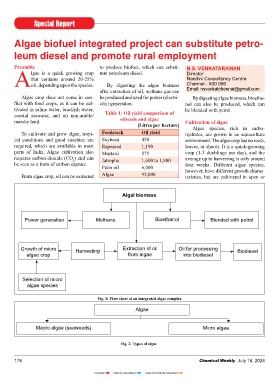
Algal biomass Mixing – to prevent sedimentation 95% of the total oil present in the algae. emissions of a major greenhouse gas.
of algae and make sure all cells are
equally exposed to light; and Supercritical fl uid extraction is a Suggested scheme for integrated
Continuous fl ow of carbon dioxide – modern technique, using supercritical complex
Power generation Methane Bioethanol Blended with petrol to enable algae to grow. carbon dioxide as solvent, and can The integrated complex should be
Table 3: Parameters for algae cultivation extract almost 100% of the oil present planned with the following facilities:
Algae farm;
in algae.
Parameter Value Oil extraction facilities for algae
Temperature (°C) 18-24 Advantages of microalgae bio-oil;
Growth of micro Harvesting Extraction of oil Oil for processing Biodiesel Salinity (gm/1) 20-24 The advantages of microalgae Transesterifi cation facility for con-
algae crop from algae into biodiesel Light intensity (lux) 2,500-5,000 cultivation are: verting algae bio-oil to algae bio-
pH 8.2-8.7 High growth rates; diesel and glycerine;
Capacity to utilise a large fraction Production of methane gas from de-
Table 4: What an integrated algae refi nery entails
Selection of micro Activity Remarks
algae species
Algae farm For cultivation of algae crop.
Oil extraction Production of algae bio-oil from algae crop.
Fig. 1: Flow sheet of an integrated algae complex
Transesterifi cation For converting algae bio-oil to biodiesel with co-production
Algae of glycerine.
Anaerobic digestion of algae biomass after extraction of oil Production of methane gas.
Macro algae (seaweeds) Micro algae Gasifi cation of biomass Production of syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO)
and hydrogen (H ), and separation of H .
2
2
Fermentation of deoiled algae mass Production of bioethanol using yeast, and blending it with
Fig. 2: Types of algae petrol.
176 Chemical Weekly July 16, 2024 Chemical Weekly July 16, 2024 177
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised