Page 184 - CW E-Magazine (8-10-2024)
P. 184
Special Report
Softer materials such as polyurethanes
and soft metals disperse the energy
of collapsing bubbles, and result in a
lower rate of damage. Figure-4 shows
the principal of cavitation in centrifugal
water pump. Figures 5,6, and 7 show
cavitation damage on a water pump
impeller blade, suction cavitation in a
centrifugal water pump impeller, and
discharge cavitation in a centrifugal
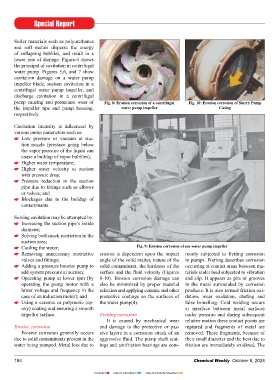
pump causing and premature wear of Fig. 8: Erosion corrosion of a centrifugal Fig. 10: Erosion corrosion of Slurry Pump
the impeller tips and pump housing, water pump impeller Casing
respectively.
Cavitation intensity is influenced by
various pump parameters such as:
Low pressure or vacuum at suc-
tion nozzle (pressure going below
the vapor pressure of the liquid can
cause a buildup of vapor bubbles);
Higher water temperature;
Higher water velocity at suction
with pressure drop;
Pressure reduction in the suction
pipe due to fittings such as elbows
or valves; and
Blockages due to the buildup of
contaminants.
Solving cavitation may be attempted by:
Increasing the suction pipe’s inside
diameter;
Solving bottleneck restriction in the
suction area;
Cooling the water; Fig. 9: Erosion corrosion of sea water pump impeller
Removing unnecessary restrictive erosion is dependent upon the impact monly subjected to fretting corrosion
valves and fittings; angle of the solid matter, nature of the in pumps. Fretting describes corrosion
Adding a pressure booster pump to solid contaminant, the hardness of the occurring at contact areas between ma-
add system pressure at suction; surface and the fluid velocity (Figures terials under load subjected to vibration
Operating pump at lower rpm (by 8-10). Erosion corrosion damage can and slip. It appears as pits or grooves
operating the pump motor with a also be minimized by proper material in the metal surrounded by corrosion
lower voltage and frequency in the selection and applying ceramic and other products. It is also termed friction oxi-
case of an induction motor); and protective coatings on the surfaces of dation, wear oxidation, chafing and
Using a ceramic or polymeric (ep- the water pump(4). false brinelling. Cold welding occurs
oxy) coating and ensuring a smooth at interface between metal surfaces
impellor surface. Fretting corrosion under pressure and during subsequent
It is caused by mechanical wear relative motion these contact points are
Erosive corrosion and damage to the protective or pas- ruptured and fragments of metal are
Erosive corrosion generally occurs sive layers in a corrosion attack of an removed. These fragments, because of
due to solid contaminants present in the aggressive fluid. The pump shaft seat- their small diameter and the heat due to
water being pumped. Metal loss due to ings and antifriction bearings are com- friction are immediately oxidized. The
184 Chemical Weekly October 8, 2024
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised