Page 183 - CW E-Magazine (8-10-2024)
P. 183
Special Report
pitting are primarily studied as electro- the electrochemical series. For example,
chemical reactions. if a weldment is different from the
parent metal, there is a risk of galvanic
Generalized corrosion, pitting and corrosion. The material used for valves,
crevice corrosion piping and the pump components must
Uniform or generalized corrosion in be studied to evaluate the risk of gal-
the pump may increase the clearances vanic corrosion in the entire system (2).
and cause the pump to lose its operat-
ing efficiency. Wear debris may simply Pitting corrosion
add to the severity. Generalized cor- It is a localised electrolytically in-
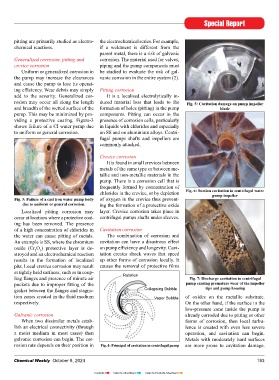
rosion may occur all along the length duced material loss that leads to the Fig. 5: Cavitation damage on pump impeller
and breadth of the wetted surface of the formation of holes (pitting) in the pump blade
pump. This may be minimized by pro- components. Pitting can occur in the
viding a protective coating. Figure-3 presence of corrosion cells, particularly
shows failure of a CI water pump due in liquids with chlorides and especially
to uniform or general corrosion. on SS and on aluminium alloys. Centri-
fugal pumps shafts and impellers are
commonly attacked.
Crevice corrosion
It is found in small crevices between
metals of the same type or between me-
tallic and non-metallic materials in the
pump. There is a corrosion cell that is
frequently formed by concentration of
chlorides in the crevice, or by depletion Fig. 6: Suction cavitation in centrifugal water
pump impeller
Fig. 3: Failure of a cast iron water pump body of oxygen in the crevice thus prevent-
due to uniform or general corrosion. ing the formation of a protective oxide
Localized pitting corrosion may layer. Crevice corrosion takes place in
occur at locations where a protective coat- centrifugal pumps shafts under sleeves.
ing has been removed. The presence
of a high concentration of chlorides in Cavitation corrosion
the water can cause pitting of metals. The combination of corrosion and
An example is SS, where the chromium cavitation can have a disastrous effect
oxide (Cr O ) protective layer is de- on pump efficiency and longevity. Cavi-
3
2
stroyed and an electrochemical reaction tation creates shock waves that speed
results in the formation of localized up other forms of corrosion locally. It
pits. Local crevice corrosion may result causes the removal of protective films
at tightly held surfaces, such as in coup-
ling flanges and presence of minute air Rotation Fig. 7: Discharge cavitation in centrifugal
pockets due to improper fitting of the pump causing premature wear of the impeller
gasket between the flanges and stagna- Collapsing Bubble tips and pump housing
tion zones created in the fluid medium Vapor Bubble of oxides on the metallic substrate.
respectively. On the other hand, if the surface in the
low-pressure zone inside the pump is
Galvanic corrosion already corroded due to pitting or other
When two dissimilar metals estab- forms of corrosion, then local turbu-
lish an electrical connectivity (through lence is created with even less severe
a moist medium in most cases) then operation, and cavitation can begin.
galvanic corrosion can begin. The cor- Metals with moderately hard surfaces
rosion rate depends on their position in Fig. 4: Principal of cavitation in centrifugal pump are more prone to cavitation damage.
Chemical Weekly October 8, 2024 183
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised