Page 186 - CW E-Magazine (26-3-2024)
P. 186
Special Report Special Report
covered in the report. In 2023 fi bres,
including woven, non-woven (mainly CA
and PTT), had the highest share with
27%. Packaging, fl exible and rigid, had
a 21% share, followed by functional
applications with 17% (mainly epoxy
resins and PUR), automotive and transport
with 10% (mainly PA, epoxy resins and
PUR) and consumer goods with 9%
(mainly PA, epoxy resins and PLA).
Building and construction had a 6%
share (mainly epoxy resins and PUR)
and electrics & electronics 5% (mainly
epoxy resins and PA). The market seg-
ments agri- and horticulture and others
had a market share of 2%, respectively.
Bio-based and non-biodegradable
polymers and biodegradable polymers Fig. 9: Shares of the produced bio-based polymers in different market segments in 2023
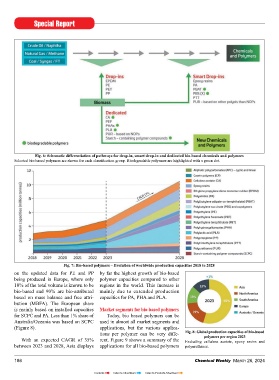
Fig. 6: Schematic differentiation of pathways for drop-in, smart drop-in and dedicated bio-based chemicals and polymers Bio-based non-biodegradable poly- Fibres: including woven and non-woven; Consumer goods: including e.g., coffee capsules, biowaste
Selected bio-based polymers are shown for each classifi cation group. Biodegradable polymers are highlighted with a green dot. mers show a CAGR of 13% until 2028 bags, leisure, interieur; Electrics and electronics: including casing; Functional: including adhesives,
(Figure 10). Here, the highest growth is coatings, cosmetics etc.; Others: including fi lms, 3D printing, medical applications, aquaculture.
expected for PA with 29%, followed by Biodegradability of polymers is compostable, but only PBSA bio-
PE and PP with 28% (combined). Bio- completely independent from the degrades also under home composting
based biodegradable polymers show an resource the polymer is made of, thus conditions and in soil, according to the
even higher growth, with 22%, compared being bio-based does not necessa- conditions defi ned in the established
to the overall bio-based polymer growth rily imply biodegradability of certain standards and certifi cation schemes.
of 17% until 2028 (Figure 11). This is polymers. PBS and copolymers such The same is true for PBAT; it is
mainly based on high growth rates for as polybutylene succinate-co-butylene industrial compostable and, for certain
PHA with 57% and PLA with 37%. adipate (PBSA) are both industrial grades, also home compostable as well
Fig. 7: Bio-based polymers – Evolution of worldwide production capacities 2018 to 2028
on the updated data for PE and PP by far the highest growth of bio-based
being produced in Europe, where only polymer capacities compared to other
10% of the total volume is known to be regions in the world. This increase is
bio-based and 90% are bio-attributed mainly due to extended production
based on mass balance and free attri- capacities for PA, PHA and PLA.
bution (MBFA). The European share
is mainly based on installed capacities Market segments for bio-based polymers
for SCPC and PA. Less than 1% share of Today, bio based polymers can be
Australia/Oceania was based on SCPC used in almost all market segments and
(Figure 8). applications, but the various applica-
tions per polymer can be very diffe- Fig. 8: Global production capacities of bio-based
polymers per region 2023
With an expected CAGR of 35% rent. Figure 9 shows a summary of the Excluding cellulose acetate, epoxy resins and
between 2023 and 2028, Asia displays applications for all bio-based polymers polyurethanes. Fig. 10: Bio-based non-biodegradable polymers – Evolution of worldwide production capacities 2018 to 2028
186 Chemical Weekly March 26, 2024 Chemical Weekly March 26, 2024 187
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised