Page 177 - CW E-Magazine (17-6-2025)
P. 177
Special Report Special Report
* Secondary/fi nal gas cooling; value product makes the process more ing and other purposes in the steel plant. present as it also takes part in the
3
* Ammonia removal; profi table. So, 330-m /THM of COG is available reaction.
* Benzol removal; for ammonia or methanol synthesis.
* Naphthalene removal; and Water wash process For the methanol synthesis reaction
* Hydrogen sulphide removal. This is the simplest and frequently Based on the Ministry of Steel with CO and CO , the stoichiometric
2
used process for ammonia stripping Annual Report (2023-24), hot metal number (Sn) of the syngas feed, which
These steps are carried out under from COG. The ammonia present in production in India was 87.045-mt. is defi ned as ((H – CO )/(CO + CO ))
2
2
2
7-kPa to 15-kPa pressures. the COG is absorbed using water and Hence, the total annual gas production should be: 2 ≤ Sn ≤ 2.1. Following this
the absorption liquor is then stripped of would on average be as follows: ratio, the CO and CO requirement
2
A summary of the process for ammonia in a distillation column using * BFG – 130,567-mscm; for the amount of H present can be
2
cleanup are given below(2)(9)(10). steam. The stream leaving at the top of * COG – 34,818-mscm; and calculated. Methane present in the
the stripper is rich in ammonia and can * LDG – 8,704-mscm. COG can be separated by adsorption
Tar removal be converted to fertilizer or anhydrous using activated carbon and the separated
Tar is a condensable vapour consist- ammonia. The quantity of H would be methane can be subjected to steam re-
2
ing mainly of aromatic hydrocarbons 20,991.7-mscm (34,818 mscm x 60.29%) forming. Steam reforming generates
ranging from volatile benzene to pitches Hydrogen sulphide removal or 1.874-mt. This is equivalent to CO along with H , which can be used
2
(which are solid at room temperature). This process is used for deep de- 50 x 1.874 = 93.71-GW of power. If for methanol production: CH + H O
2
4
Tar can be removed as a saleable sulphurization of steel plant gases. It electrolysers were used for hydrogen CO + 3H
2
material that can be further processed in is generally used after another desul- production, 93.71-GW would be the
a tar distillation plant. Around 70% of phurization process – like alkanolamine savings in solar PV systems. This is the The production of ammonia
the tar is condensed when sprayed with or Selexol process. In this process, the potential for H . requires N and H in the ratio of 1:3.
2
2
2
liquor. Further, 20% is removed at steel plant gases are passed through a N is obtained using suffi cient quantity
2
the primary cooler and the remaining bed of zinc oxide (ZnO) at high tempera- The utilization of these gases would of BFG, by separating N from CO
2
10% in electrostatic tar precipitators. tures where the H S reacts with ZnO require converting them to other profi t- and CO . CO and CO can be used for
2
2
2
to produce ZnS. able chemicals, which in most cases methanol production as COG alone
Ammonia removal require H . The possibilities are con- does not have suffi cient CO for methanol
2
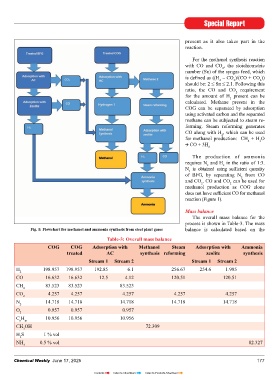
Ammonia removal from COG is Generation of gases in a steel plant version to methanol, ammonia, and reaction (Figure 1).
done mainly using the following three In a typical steel plant, the quantity certain chemicals that can be made
methods: of byproduct gases generated per tonne utilizing CO or CO and methanol, Mass balance
2
of hot metal (THM) are(9)(10): etc. The entire process requires that The overall mass balance for the
Ammonium sulphate process * BFG – 1,200-2,000-m /THM the components of steel plant gases be process is shown in Table-3. The mass
3
There can be a few variations in (average: 1,500-m /THM) separated, as required by the process Fig. 1: Flowchart for methanol and ammonia synthesis from steel plant gases balance is calculated based on the
3
this process, but it basically involves * COG – 300-500-m /THM (average and then reacted to give the desired
3
sulphuric acid and COG to be contacted 400-m /THM); and chemical. Table-3: Overall mass balance
3
to form ammonium sulphate. * LDG – 80-150-m /THM (100-m / COG COG Adsorption with Methanol Steam Adsorption with Ammonia
3
3
THM). Case 1: Production of methanol and treated AC synthesis reforming zeolite synthesis
Phosam process ammonia. Stream 1 Stream 2 Stream 1 Stream 2
The process uses a solution of It is also assumed that around 70-m / Methanol synthesis requires a combi-
3
mono-ammonium phosphate for absorbing THM of COG will be used for heat- nation of H and CO; CO can be H 2 198.957 198.957 192.85 6.1 256.67 254.6 1.985
2
2
ammonia, forming di- and tri-phosphate CO 16.632 16.632 12.5 4.12 120.51 120.51
salt solution. The process is reversed Table-2: Composition of gases produced per tonne of steel CH 83.523 83.523 83.523
by stripping with high pressure steam Component BFG (m /THM) Vol% COG (m /THM) Vol% 4
3
3
to obtain anhydrous ammonia. An alter- CO 340.8 22.72 16.632 5.04 CO 2 4.257 4.257 4.257 4.257 4.257
native is the production of diammonium CH 0 0 83.523 23.86 N 2 14.718 14.718 14.718 14.718 14.718
phosphate for fertiliser use. 4 O 0.957 0.957 0.957
CO 2 317.7 21.18 4.257 1.28 2
Using the Phosam process, ammonia N 2 802.5 53.50 14.718 4.46 C H m 10.956 10.956 10.956
n
found in raw coke oven gas can be O 0 0 0.957 0.273 CH OH 72.309
3
2
converted into commercially pure C H 2.7 0.19 10.956 3.13 H S 1 % vol
anhydrous ammonia. Compared to n m 2
ammonium sulphate operations, this high- 1,500 330 NH 3 0.5 % vol 82.327
176 Chemical Weekly June 17, 2025 Chemical Weekly June 17, 2025 177
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised