Page 191 - CW E-Magazine (8-4-2025)
P. 191
Special Report Special Report
Process safety and risk management (Part 4): Table 2: Ready reckoner for taking PHA decisions
Phase/Stage of PHA What-if FMEA HAZOP FTA QRA
Process Hazards Analysis and Facility Siting Project Development checklist
X
of basic data
There’s an old saying that if you To identify all recognized and Pre-authori- X O O
think safety is expensive, try an unrecognized hazardous events; JOY M. SHAH sation
“ accident. Accidents cost a lot To identify hazardous materials and Founder and Chief Consultant Design X O O O O
Innov8 ProTech Solutions
of money. And, not only in damage to hazardous processes; Former Sr. Vice President – Technical Baseline PHA of new facility X O O O O
plant and in claims for injury, but also To provide framework for under- Reliance Industries Ltd. Cyclic PHA of existing facility X O O O
in the loss of the company’s reputa- standing the hazardous events and E-mail: joymshah@gmail.com Process Changes/MOC X O O O
tion.”– Dr. Trevor Kletz responses to them; Decommissioning and mothballing X
To work out actions to eliminate PHA is also carried out for existing (X) denotes minimum requirement; (O) depicts optional method.
Process Safety and Risk Manage- and/or reduce risks involved with facilities: once in fi ve years in medium hazards
ment is a comprehensive approach hazards; Cyclic analysis, for which the facilities, and once in 10 years in low
for goal zero incident, zero injury and To understand consequences or frequency depends on hazards; hazards facilities.
zero environmental release. In previous impact on other PSM elements; Revalidation of previous review
three notes, I have discussed on lead- To seek to achieve a multi-disciplined depending on hazards of operation; Methodology for PHA
ership aspects of Process Safety and consensus on hazard control; and and There are many methodologies
Risk Management. In next three notes, To document results for future use. Technology and facilities changes. for conducting PHA. They can be
I shall discuss on three most important either qualitative or quantitative. They
elements related to chemical engineers: PHA is carried out for new process PHA is also important to sup- can be used alone or in combination,
1. Process hazards analysis and faci and facilities with several reviews port incident investigation and dur- depending on requirement. Some of
lity siting; during different stages of development ing decommissioning, mothballing the popular methods are listed in
2. Incident investigation and learning including: and/or dismantling of process faci- Table 1.
from incident; and Screening in early development stage; lities.
3. Risk management for sustainable Design review at design completion; Based on my experience, 95-97%
operation. Final project safety report, before Apart from initial base line PHA, of hazardous events can be identifi ed
start-up; and the recommended best practice is to by What If/Checklist and/or HAZOP,
There are few other aspects of Baseline PHA, after any start-up carry out cyclic PHA at least once in 3-5% require FMEA, and <1% require
execution part related to chemical engi- changes. three years for high-hazards facilities, FTA or QRA.
neers: Pre-start up safety audit; Process Table 1: Methodologies to conduct PHA
technology information, operating pro- Qualitative techniques Quantitative techniques One question that often comes up
cedures; and Management of Change. is: ‘Which method need to be applied?’
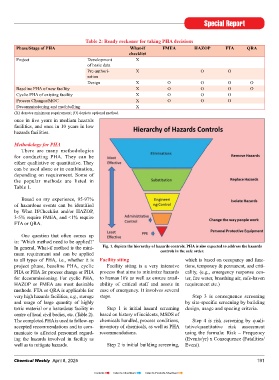
What If/Checklist Uses “what if” Fault Tree Analysis Quantitative In general, What-if method is the mini- Fig. 1. depicts the hierarchy of hazards controls. PHA is also expected to address the hazards
This note addresses the aspects of questions to evaluate (FTA) method to deter- mum requirement and can be applied controls in the safe order.
Process Hazards Analysis (PHA) and effect of occurrences mine probability to all types of PHA, i.e., whether it is Facility siting which is based on occupancy and func-
Facility Siting. on people/things of an undesired project phase, baseline PHA, cyclic Facility siting is a very intensive tions, temporary & permanent, and criti-
outside the process “top event” PHA or PHA for process change or PHA process that aims to minimize hazards cality, (e.g., emergency response cen-
Process Hazards Analysis (PHA) Hazard and Guide-word driven Quantitative Risk Quantitative for decommissioning. For cyclic PHA, to human life as well as ensure avail- ter, fi re water, breathing air, safe-haven
PHA is a method to identify, evalu- Operability Study review of hazards, Analysis (QRA) method to deter- HAZOP or FMEA are most desirable ability of critical staff and assets in requirement etc.)
ate, as well as develop methods to (HAZOP) its consequences mine extent of methods. FTA or QRA is applicable for case of emergency. It involves several
control the hazards in the process unit. and mitigation plan risk to plant per- very high hazards facilities, e.g., storage steps. Step 3 is consequence screening
It includes hazard identifi cation, con- sonnel, as well as and usage of large quantity of highly by site-specifi c screening by building
to nearby
sequence analysis, hazard evaluation, community. toxic material or a hazardous facility in Step 1 is initial hazard screening design, usage and spacing criteria.
human factors, facility siting & inher- centre of local civil bodies, etc. (Table 2). based on history of incidents, MSDS of
ently safer process evaluation. Failure Mode and Identifi es failure The completed PHA is used to follow-up chemicals handled, process conditions, Step 4 is risk screening by quali-
Effect Analysis modes of equip- accepted recommendations and to com- inventory of chemicals, as well as PHA tative/quantitative risk assessment
For every hazardous manufacturing (FMEA) ment and develops municate to affected personnel regard- recommendations. using the formula: Risk = Frequency
facility, PHA is important aspect with risk estimate for ing the hazards involved in facility as (Events/yr) x Consequence (Fatalities/
prioritizing action
following objectives: well as to mitigate hazards. Step 2 is initial building screening, Event).
190 Chemical Weekly April 8, 2025 Chemical Weekly April 8, 2025 191
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised