Page 189 - CW E-Magazine (28-11-2023)
P. 189
Special Report Special Report
COMPREHENSIVE CARBON MANAGEMENT importance of carbon manage- to-meet-its-2045-net-zero-target/] www.wirtschaft.nrw/sites/default/
ment. The umbrella term includes The Offi ce of Carbon Manage- files/documents/mwide_br_car-
New thinking and terminology required to achieve climate not only the capture and storage ment’s mission is to facilitate a just bon_management_strategie_sum-
of CO (carbon capture and stor- and environmentally sustainable mary_eng_bf.pdf)].
2
targets and secure a sustainable carbon supply age, CCS), but also CO capture transition toward a net-zero carbon
2
and utilisation (carbon capture and economy. How do we do this? By To limit carbon management to the
omprehensive carbon manage- nature cannot be decarbonised. Even CHRISTOPHER VOM BERG, utilisation, CCU) as well as the focusing on carbon dioxide – its management of CO is not adequate be-
2
ment goes beyond carbon di- in the energy sector, some applications removal of CO from the atmo- storage, containment, and capture. cause it misses the entire aspect of raw
2
Coxide (CO ) emissions, capture like aviation or shipping will not MICHAEL CARUS & LARA DAMMER sphere (carbon dioxide removal, [Trace carbon neutral organisation; material supply of carbon and circular
Renewable Carbon Initiative (RCI)
2
and long-term storage. It decouples the be electrifi ed in the foreseeable future Renewable-carbon-initiative.com CDR). [Stiftung Wissenschaft und https://www.our-trace.com/carbon- economy.
whole industry from fossil feedstock, and require carbon-based fuels. In these Politik; https://www.swp-berlin. neutral/carbon-management].
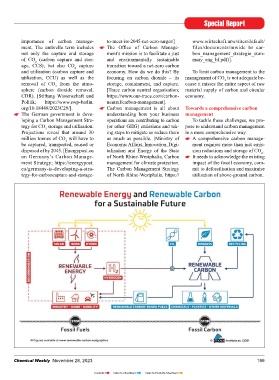
eliminates the use of fossil carbon sectors, the embedded carbon – the car- other conversions to CO before release org/10.18449/2023C29/]. Carbon management is all about Towards a comprehensive carbon
2
wherever possible and allocates renew- bon bound in the molecules – is a key to the atmosphere. In the US, CO and The German government is deve- understanding how your business management
2
able carbon (from biomass, CO and element to enable sustainable carbon CO are grouped together as “carbon loping a Carbon Management Stra- operations are contributing to carbon To tackle these challenges, we pro-
2
recycling) as effi ciently and effectively cycles. It cannot be substituted. The oxides” for purposes of Section 45Q tegy for CO storage and utilisation. (or other GHG) emissions and tak- pose to understand carbon management
2
as possible where carbon use is unavoid- dominant feedstock for these materials, CCUS tax credits. Projections reveal that around 30 ing steps to mitigate or reduce them in a more comprehensive way.
able. The aim is to achieve the lowest fossil carbon, can however be replaced million tonnes of CO will have to as much as possible. [Ministry of A comprehensive carbon manage-
2
possible CO emissions, reducing the with alternative carbon sources not Current focus is on CO management be captured, transported, reused or Economic Affairs, Innovation, Digi- ment requires more than just emis-
2
2
need for CO removal to achieve net derived from fossil feedstock. only – not on comprehensive carbon disposed of by 2045. [Energypost.eu talization and Energy of the State sion reductions and storage of CO .
2
2
zero, and to provide a secure supply of management on Germany’s Carbon Manage- of North Rhine-Westphalia, Carbon It needs to acknowledge the existing
renewable carbon to all dependent Based on available IEA and IPCC The above challenge requires com- ment Strategy; https://energypost. management for climate protection. impact of the fossil economy, com-
industries such as chemicals and mate- scenarios, the only way to reach climate prehensive carbon management, which eu/germany-is-developing-a-stra- The Carbon Management Strategy mit to defossilisation and maximise
rials. Only when carbon is recognised as neutrality is to move away from fossil also considers aspects like supply and tegy-for-carboncapture-and-storage- of North Rhine-Westphalia. https:// utilisation of above-ground carbon.
a raw material in carbon management fuel as soon as possible. In Europe, demand, and the sustainability of car-
strategies can truly sustainable carbon 93% of the carbon embedded in the bon as a feedstock. But again, much of
cycles be achieved. With a proper com- chemical and derived materials indus- the current focus of carbon manage-
prehensive carbon management, the try comes from fossil oil, gas and coal. ment is on the energy sector, in particu-
carbon-reliant material and energy sec- Using fossil carbon from the ground is lar on CO abatement and carbon cap-
2
tors will be defossilised and the remain- the main reason for human-made cli- ture combined with long-term storage.
ing energy sector will be decarbonised. mate change. The challenge is therefore Developing a sustainable carbon sup-
to cover this (globally still growing) ply chain to embed in products and to
And only for the remaining share carbon demand by using sources which create sustainable carbon cycles mostly
of truly unavoidable emissions, CO 2 already are ‘above the ground’ – this remains a side aspect in current policy
removal and carbon capture and storage is either biomass (from the biosphere), and is often not followed up with con-
should come into play. CO (1) (from the atmosphere and from crete action yet. For example, the on-
2
biogenic as well as fossil point sources) going public consultation on industrial
The focus of climate policy has and recycling (from the technosphere) – carbon management reduces carbon
been, and to large degrees continues to establish sustainable carbon cycles. management to carbon capture and the
to be, on the decarbonisation of the management of CO .
2
energy sector, where signifi cant progress Such a defossilisation strategy is key
in using alternative energy sources like to reduce the use of and dependence on We have collected several current
solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal fossil fuels. Defossilisation (by means carbon management defi nitions that
coupled with green hydrogen as of renewable carbon) reduces the need narrow down the topic to CO emis-
2
energy carrier has been achieved. Here, to extract additional fossil carbon from sions and carbon capture with long-
decarbonisation is the correct term the ground – which is the main cause of term storage, as below:
because all these options do not rely human made climate change.
on carbon-based fossil feedstock. In Climate policy in the European
contrast the products of industrial sec- The use of the term CCU generally Union (EU) and Germany changed
tors like chemicals, derived materials, refers to the utilisation of CO , but can signifi cantly with the adoption of
2
plastics and construction products are also include industrial carbon mon- net-zero emissions targets. A key
principally carbon-based and by their oxide (CO) sources prior to fl aring or new development is the growing
188 Chemical Weekly November 28, 2023 Chemical Weekly November 28, 2023 189
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised