Page 176 - CW E-Magazine (7-11-2023)
P. 176
Special Report
fouling with operating time of the shell
Flow direction and tube heat exchanger is shown in
DEPositioN REmovAL Figure-3.
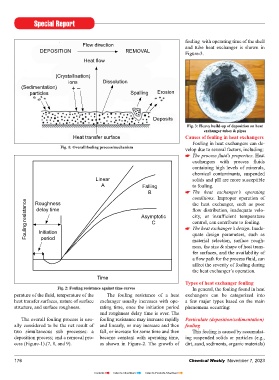
Heat flow
(Crystallisation)
ions Dissolution
(sedimentation) + –
particles spalling Erosion
Deposits
Fig. 3: Heavy build-up of deposition on heat
exchanger tubes & pipes
Heat transfer surface Causes of fouling in heat exchangers
Fouling in heat exchangers can de-
Fig. 1: Overall fouling process/mechanism velop due to several factors, including:
The process fluid’s properties. Heat
exchangers with process fluids
containing high levels of minerals,
chemical contaminants, suspended
Linear solids and pH are more susceptible
A Falling to fouling.
B The heat exchanger’s operating
conditions. Improper operation of
Fouling resistance delay time Asymptotic The heat exchanger’s design. Inade-
Roughness
the heat exchanger, such as poor
flow distribution, inadequate velo-
city, or insufficient temperature
C
control, can contribute to fouling.
initiation
quate design parameters, such as
period
material selection, surface rough-
ness, the size & shape of heat trans-
fer surfaces, and the availability of
a flow path for the process fluid, can
affect the severity of fouling during
the heat exchanger’s operation.
time
Types of heat exchanger fouling
Fig. 2: Fouling resistance against time curves In general, the fouling found in heat
perature of the fluid, temperature of the The fouling resistance of a heat exchangers can be categorized into
heat transfer surfaces, nature of surface exchanger usually increases with ope- a few major types based on the main
structure, and surface roughness. rating time, once the initiation period phenomena occurring:
and roughness delay time is over. The
The overall fouling process is usu- fouling resistance may increase rapidly Particulate (deposition/sedimentation)
ally considered to be the net result of and linearly, or may increase and then fouling
two simultaneous sub processes: a fall, or increase for some time and then This fouling is caused by accumulat-
deposition process; and a removal pro- become constant with operating time, ing suspended solids or particles (e.g.,
cess (Figure-1).(7, 8, and 9). as shown in Figure-2. The growth of dirt, sand, sediments, organic materials)
176 Chemical Weekly November 7, 2023
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised