Page 194 - CW E-Magazine (22-4-2025)
P. 194
Special Report Special Report
2. Lossof employee lives; tion level, train all team members, carry 3. Third party audit by external party
3. Loss to environment; and out risk assessment, prepare risk and con- not conversant with the people.
4. Loss to general public. trol register, establish assessment and audit
protocol, as well as create a culture of risk- It is essential that all three levels
Convert all these to overall business based decision-making process. These are aligned for integrated assurance.
loss for each risk criteria and defi ne it elements are briefl y described below.
as a tolerable or intolerable risk. Con- Creating culture for risk-based
sider both direct and indirect losses. Team formation decision making process
Alternatively, prepare Risk Assessment Plant level risk assessment team is As in the story of “Blind Men and
Matrix (RAM) as given below and posi- always cross-functional, including Risk an Elephant”, each employee perceives
tion incident in the right block. Benefi ts Expert, Design, Process, Operation, risk management differently. When
and drawbacks of RAM are as follows: Maintenance (Mechanical, Electrical, every employee perceives it same, it
1. It enables consistent approach to Instrumentation, Civil, etc), safety and becomes their belief and thereby a culture.
qualitative risk assessment; and business experts. This team reports to It becomes deeply held assumptions,
2. It establishes a common termino- site level management team and all site beliefs and values with respect to risk
logy to support communication level risk management teams reports management shared by an organisation’s
about risk. to corporate/board level team. Plant employees. Risk culture is required to
level team is not only responsible for nudge employees towards right behaviour,
RAM is to usedin accordance with execution, but also for creating culture prevent bad things from happening, as
certain fundamental principles: amongst staff members for risk-based well as fulfi l regulatory obligations.
3. It refers only to the specifi c risks to decision-making processes. All team Development of culture starts with policy,
determine how to categorise; and members are trained by external expert procedure and systems. Proper training
4. It does not generate decision about and rest of staff members are trained and association of right team members
actions that should be taken. by site level risk management team. make it smooth sailing. Demanding
risk assessment and risk-based decision
No two companies have the same Risk and control register preparation by authority will make employees to
risk tolerance, and every company must Risk and control register isprepared think in that direction. Once all such
develop their own based on their busi- for every unit, plant, site as well as elements are in place, we can say that
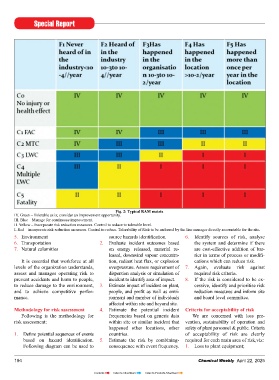
Fig. 2: Typical RAM matrix ness tolerance. Experts can help develop organisation as a whole. It consists of name Risk Management process is evolving.
IV. Green – Tolerable as is; consider an improvement opportunity. such matrix based on risk tolerance of unit; purpose of risk register;type
III. Blue – Manage for continuous improvement. To achieve maturity in risk man-
II. Yellow – Incorporate risk reduction measures. Control to reduce to tolerable level. capabilities. If similar incident is heard and name of risk, risk owner, risk cate- agement framework, following para-
I. Red – incorporate risk reduction measures. Control to reduce. Tolerability of Risk to be endorsed by the line manager directly accountable for the site. in industry and lead to single Lost Work- gory; Risk source, causes and its cate- meters are evaluated for its status in an
5. Environment source hazards identifi cation. 6. Identify sources of risk, analyse day Case (LWC) the classifi cation is blue gory as well as consequences and its organisation, viz, Basic, Developing,
6. Transportation 2. Evaluate incident outcomes based the system and determine if there (F2C3-Tolerable with improvement category; worst credible scenario; Risk Established, Advanced and Optimised:
7. Natural calamities on energy released, material re- are cost-effective addition of bar- proposals) but if it is repeated at same response and mitigation plan; details of 1. Risk governance
leased, downwind vapour concentra- rier in terms of process or modifi - location, it becomes Red (F4C3) and In- loss;control attributes of risk, as well as 2. Risk management capability and
It is essential that workforce at all tion, radiant heat fl ux, or explosion cations which can reduce risk. tolerable risk. It is to be reported to line details of residual risk, its remediation competency
levels of the organization understands, overpressure. Assess requirement of 7. Again, evaluate risk against manager directly accountable for site. measuresand its future impact. From 3. Risk integration
assess and manages operating risk to dispersion analysis or simulation of required risk criteria. Organisation have to fi nd action plan to various criteria, it will pop up whether it is 4. Risk identifi cation and assessment
prevent accidents and harm to people, incident to identify area of impact. 8. If the risk is considered to be ex- reduce it to tolerable level, i.e., to avoid controllable or uncontrollable risk as well 5. Risk responses
to reduce damage to the environment, 3. Estimate impact of incident on plant, cessive, identify and prioritise risk such incidence. The above mentioned is as tolerable and intolerable risk. Based on 6. Risk response – compliances
and to achieve competitive perfor- people, and profi t as well as envi- reduction measures and inform site very basic matrix. Now more and more risk register, residual risk heat map can be 7. Risk monitoring – self-verifi cation
mance. ronment and number of individuals and board level committee. complex matrices with different types of prepared for visualisation of risk tolerance 8. Risk monitoring – functional assurance
affected within site and beyond site. consequences, e.g., environment, fi nan- of the site or organisation. 9. Risk monitoring – independent assurance
Methodology for risk assessment 4. Estimate the potential incident Criteria for acceptability of risk cial loss, and reputation, are developed.
Following is the methodology for frequencies based on generic data We are concerned with loss pre- Establishing assessment and auditprocess The criteria for each parameter are
risk assessment: within site or similar incident that vention, sustainability of operation and Risk Management There are three level of assessment, viz.: well defi ned and gap analysis can be
happened other locations, other safety of plant personnel & public. Criteria Risk Management is a buzzword for 1. Self-verifi cation by executor or done for continuous improvement. Once
1. Defi ne potential sequences of events countries. of acceptability of risk are clearly safe and sustainable operation. For effec- his/her peers. It is line verifi cation; risk management and risk-based decision
based on hazard identifi cation. 5. Estimate the risk by combining- required for each main area of risk,viz: tive risk management, organisation need 2. Functional assurance by subject making culture is mature, it is expected
Following diagram can be used to consequence with event frequency. 1. Loss to plant equipment; to make team from Board level to execu- matter expert; and to achieve safe and sustainable operation.
194 Chemical Weekly April 22, 2025 Chemical Weekly April 22, 2025 195
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised