Page 174 - CW E-Magazine (7-5-2024)
P. 174
Special Report Special Report
better workplace safety and achieve over two decades to optimise its ope- instant, run a software model, and rosion, its progress, and the impact of Organisations with good governance To tackle emerging attacks, such
environmental targets. A digital twin is rations and drive enterprise-wide predict an imminent underperformance the vulnerabilities of varying process processes can practice security-by- as the rise in cyber-physical threats, in
a virtual model of an asset (compressor) performance. Indeed, a wedding of or failure. parameters must be understood through design – building systems and pro- process plants such as a fertiliser faci-
or process (synthesis), uses IoT operational technology (OT) and advanced monitoring techniques. In cesses able to respond to unexpected lity, companies need to build agility into
sensors to monitor and capture data information and communication The shift from reactive (‘run to fail- fact, we may have to prioritise inspec- risks and emerging dangers. Employee their cybersecurity practices and ap-
from physical objects, process it in technology (ICT) can result in a ure’) to reliability centred maintenance tions, strengthen predictive capabilities awareness is also a crucial frontline proaches so that they can react quickly
real-time in combination with histori- saving potential of the order of (RCM) has been gradual but avoided with regards to corrosion by improving defense, building cybersecurity con- when the time comes. As cyberattacks
cal data to provide an elaborate view 25% on avoidable costs. costly equipment failures. Today’s upon data evaluation and better deci- sciousness and password discipline to and breaches of digitised data are be-
on the performance of manufacturing pro-active or predictive maintenance sion making using accurate and real protect against the relentless malware coming common, the risk of fraud for
equipment and plants. These models Maintenance strategy programmes use advanced AI-based time data. and phishing campaigns. businesses and institutions is increasing.
are combined with advanced visuali- Historically, operators and mainte- analytics to identify the predominant It could bring potential damage to
sation technologies and data analytics nance men are trained by the original factors and monitor parameters to fi x Most of the present-day non-de- The EY 20th Global Information critical systems and infrastructure such
to fast-track troubleshooting, forecast equipment manufacturers (OEM) to variations leading to failures – abrupt structive techniques used in fertiliser Security Survey shows that rising digi- as power generation facilities, process
imminent failures, and innovate equip- maintain operations as intended by the or incipient. Moreover, advanced pre- plants for corrosion inspection are tisation and IIoT are increasing the control systems, etc. Therefore, an
ment and retrofi t the same in an exist- designer as far as possible. During daily dictive systems are capable of accurately costly and are likely to invite added complexity of the threat landscape. effective information security manage-
ing facility. Often, a low turndown inspection rounds in search of abnormal predicting remaining life of furnace risk and downtime. Traditional inspec- To protect critical information, an ment system (ISMS) is necessary to
ratio arising out of overdesign in size behaviour of process and equipment tubes and likely failure time of rotating tion techniques are built on design organisation must not only address the defend facilities against cyberattacks
and capacity of equipment is a generic and other factors which may run down equipment. With this, operators are data and operating parameters and security of the traditional IT and OT and other malicious data breaches. The
problem associated with design. These effi ciency of plant operation they list empowered to extend equipment ser- are likely to evade remote locations environments, it must also deal with standard ISO/IEC 27001 provides a de-
data-driven models in the virtual envi- out the immediate as well as long term vice life, avoid expensive repairs, and such as buried pipes or equipment the added complexities from the IIoT, tailed framework for the development,
ronment also provide the requisite maintenance requirements. OEMs, on minimise unscheduled downtime. located in trenches or covered under while also integrating innovative digi- implementation, and maintenance of
inputs to better future designs. Digital the other hand, manufacture and deli- insulation. Digital corrosion manage- tal business process disruptors, such as just such a system. Certifi cation to ISO/
twins are used in brownfi eld projects ver equipment with utmost reliability, Corrosion management ment techniques empower companies robotic process automation, blockchain IEC 27001 can reduce overall informa-
to guide the revamp and modernisa- taking into account the facility owner’s NACE International puts the annual to go beyond traditional inspection and AI. Never before has it been so tion security risks, ease compliance
tion of existing facilities to capture requirement of balanced throughput, cost impact of corrosion in the process- and maintenance activities to achieve important to ensure that security efforts with applicable security regulations
better operating effi ciencies. A recent energy effi ciency, asset integrity, safety ing industry alone at $50-bn. A 30% optimum performance across the unit. are integrated into every facet of an and requirements, and boost the organisa-
Gartner survey suggests that nearly and long service life. Even with a savings on adoption of best practices By using a digitally-enabled corrosion organisation’s operations. tion’s security culture.
half of all organisations implementing highly optimised design, the shop fl oor in corrosion prevention will come to management approach, companies can
IoT technologies were currently using performance of the equipment may ex- $15-bn, which is signifi cant. Beyond develop a holistic, proactive, and EY ‘cyber fusion’ lists three level Turnaround management
or were planning to use digital twins. perience certain voids, needing design economics, corrosion also adversely cost-effective maintenance & inspec- of cyber-attacks and suggest reme- Turnarounds inevitably contribute
According to a recent research report, improvements or else to be overcome affects plant reliability, leads to acci- tion plan, and strategies for corrosion dies thereof. They are the common, to bulk of the downtime in operating
the market value of digital twins is through a modifi ed operating philosophy. dents, damages assets, and spoils the abatement. advanced, and emerging attacks. The plants. Completion of turnarounds with-
estimated to grow from $3.8-bn in 2019 Analysis of real time operating data environment. Fertiliser plants are abun- common attacks by hawkers, prevented out time and cost overruns is dependent
to $35.8-bn by 2025. Companies like captured by monitoring systems will dantly prone to corrosive effects. Data security by means of point solutions, remain a on ensuring the right and necessary
Royal Dutch Shell are harnessing the help the operator to ascertain devi- In the digital world, data security key element of cybersecurity resilience, information, supplies, equipment and
power of digital transformation for ation in machine condition at the right Therefore, early detection of cor- is a prime consideration and responsi- with tools including antivirus software, manpower at the right time. Therefore,
bility of management. While current intruder detection and protection sys- a lot of planning and scheduling is to
Systems operating data is relevant for day-to- tems, consistent patch management be done before shutting down a produc-
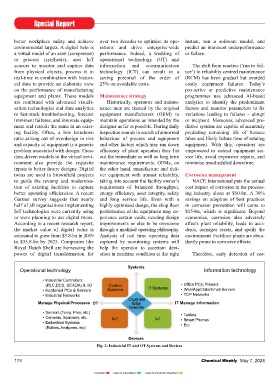
Operational technology Information technology day business, historical data is useful and encryption technologies to protect tive plant for purposes of inspection of
• Industrial Controllers for policy formulation and prediction the integrity of data, even if an attacker vessel internals, catalyst change, equip-
(PLC,DCS, SCADA) & I/O Control • Offi ce PCs, Printers of price and market trends. Maintain- does gain access to it. A prudent threat ment replacement, cleaning of fouled
• Hardened PCs & Servers Systems IT Systems • Web/App/Data/Email Servers ing the confi dentiality and integrity detection and response capability may equipment or hooking up retrofi t sys-
• Industrial Networks • TCP Networks of the data are important from the be called as a security operation centre tems to ensure reliability of plant as-
Cloud and
Manage Physical Processes OT Edge IT Manage Information security point of view. Digitisation and (SOC), and is an excellent defence sets and ward off unexpected failures.
Networks encryption help to protect the organi- against advanced attacks. SOCs are Most often turnarounds incur time and
• Sensors (Temp, Pres, etc.) • Tablets sation’s electronic information sys- active defence guards – a deliberately cost overruns due to faulty projections
• Cameras, Scanners, etc. IIoT IoT • Smart Phones
• Embedded Systems • Etc. tems from attack of hackers and pre- planned and continuously executed based on inadequate and primitive in-
(Robots, Analyzers, etc) vent unauthorised access. Increased campaign that aims to identify and formation about the condition of equip-
digitisation in the oil and gas industry, remove hidden attackers and defeat likely ment, delivery schedule of critical sup-
Devices besides improving profi tability, also threat scenarios targeting the organi- plies, assessment of quantum of work
Fig. 2: Industrial IT and OT Systems and Devices raises concerns of cybersecurity risks. sation’s most critical assets. involved and manpower accounted.
174 Chemical Weekly May 7, 2024 Chemical Weekly May 7, 2024 175
Contents Index to Advertisers Index to Products Advertised